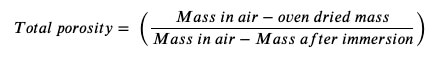What is Water porosity testing?
Water porosity testing measures the density and total water porosity of cores from concrete structures to assess their durability and resistance to the ingress of water and the damaging compounds held within such as carbonate or chloride ions.
How does Water porosity testing work?
The water porosity is measured from a broken core taken from a concrete element. The dry and saturated weight of the samples are used to calculate the total porosity
Water porosity of concrete is directly related to the durability of concrete especially through mechanisms caused by the ingress of substances into the concrete such as carbonation, chloride attack etc.
What is Water porosity testing used for?
Deterioration process | Defects | Control of repairs |
Complementary technique which can be |
How do I carry out Water porosity testing?
There are various standards that provide detailed testing methodologies for the determination of water porosity such as BS EN 1881 Part 122 and RILEM CPC 11.3. However, it should be noted that the procedures described vary in preparation of specimens, testing conditions and process of testing.
A simple step by step guide based on RILEM CPC 11.3 would be as follows:
A coring schedule must be developed based on the test objectives and completed based on correct sampling procedures . This could be a systematic random sampling of an entire structure or a targeted investigation of specific areas at risk of carbonation and corrosion.
Concrete cores are transported to the laboratory and oven dried at 105 °C until a constant mass is reached.
After removal from the oven cores are weighed and stored in a vacuum chamber.
After 24 hours conditioning water is added to the vacuum chamber and pressure maintained for another 2 hours.
The cores are then removed from the water and re weighed.
The measured mass before immersion is subtracted from the mass after immersion to calculate the mass of absorbed water.
The total porosity percentage is then calculated using Equation 1.
What equipment and expertise are required for Water porosity testing?
Equipment required for the Water porosity test to RILEM CPC 11.3 includes:
A precise electronic scale capable of measuring to at least 0.1 gram for weighing the samples.
- An oven capable of maintaining a set temperature, usually around 105°C, for drying the samples to constant weight.
- A vacuum chamber and pumps for sample conditioning.
The water porosity test is relatively simple to carry out and but does require testing expertise and experience in the use of vacuum conditioning. Careful sample preparation, weighing of samples and data analysis is required.
What are the advantages of Water porosity testing?
Combined with an intelligent coring scheme the test offers a detailed representation of concrete porosity, density and durability.
Low costs.
By focusing on vacuum saturation, the RILEM CPC 11.3 test achieves unparalleled precision in detecting even minute porosity variations.
This technique is sensitive to subtle changes in the concrete matrix, enabling the detection of early signs of deterioration not visible during visual inspection.
Density measurement allows assessment of placement and batching quality as low densities are often indicative of poor compaction and honeycombing, excessive water addition or under batching of certain materials.
What are the disadvantages of Water porosity testing?
The test requires specialised laboratory equipment such vacuum systems and samples must undergo a complex conditioning process.
The more intricate sample preparation and testing procedures of RILEM CPC 11.3 compared with RILEM CPC 11.1 or BS EN 1881 Part 122 mean longer lead times from sample preparation to obtaining results.
Technical expertise and laboratory experience are required for sample preparation and testing.
The test is destructive in nature using cores cut from the structure being tested. This limits the number of tests that can be completed, the areas that can be tested and the frequency of testing. Repairs can be costly and time consuming.
How accurate is Water porosity testing?
This test is accurate to 1 % of the total porosity of the concrete tested.
What are the limitations of Water porosity testing?
The fact specialised lab equipment and experience are required to carry out the test, the length and complexity of the testing process and the destructive nature of the test may limit the suitable applications and feasible number of water porosity tests that can be carried out.
Equipment specificity can also introduce result variability, a challenge for maintaining consistency across different settings. The equipment essential for this method requires regular maintenance and calibration, adding to operational costs and complexity.
The intricate nature of the procedure increases the risk of technical errors, which can compromise data accuracy and reliability.
Ancillary information
Maturity of test: > 10 years
Qualification & interpretation : Specialised lab
Service disruption: No
Preliminary works: Yes
Time consumption Medium ( one day)
Cost Low
Access to element 2 faces